A Guide to SEO Website Structure
Introduction
If you’ve ever wondered why some websites effortlessly appear on the first page of Google while others get buried on page ten, the answer is often website structure. Most students learning SEO focus on keywords, backlinks, and content creation all important elements. But without the right structure, even the most well-written pages can struggle to rank. Think of your website like a library: if books aren’t organized, readers never find what they’re searching for. The same goes for Google’s crawlers.
In the last few years, especially after Google’s 2023–2025 algorithm updates, website structure has become a powerful ranking factor. Google now prioritizes sites that offer clarity, context, and simplified navigation because these elements improve user experience and help algorithms understand content relationships. This means that a well-planned SEO website structure is not just “good practice” it’s essential for visibility.
In this guide, you’ll learn how to create a website structure that search engines understand and users love. We’ll break down technical concepts into simpler explanations, offer real-world examples, and give you actionable steps you can apply immediately even if you’re a beginner. By the end, you’ll be able to architect a site that is organized, scalable, and truly SEO-friendly.
Why Website Structure Matters in SEO
Google’s mission has always been to deliver the most relevant information to users as quickly as possible. Website structure directly contributes to this by:
-
Helping Google crawl pages efficiently
-
Making content connections clear through internal linking
-
Reducing bounce rates with intuitive navigation
-
Allowing pages to build topical authority
A clean structure is also crucial for Google’s Knowledge Graph, entity relationships, and semantic SEO — all major parts of Google’s latest updates.
A data point worth noting:
According to Backlinko’s 2023 analysis of 11 million SERPs, websites with strong internal linking and clear architecture consistently ranked higher than those with chaotic navigation.
This isn’t surprising. When your structure makes sense, Google trusts your site more. And trust is everything in SEO.
The Fundamentals of SEO-Friendly Website Structure
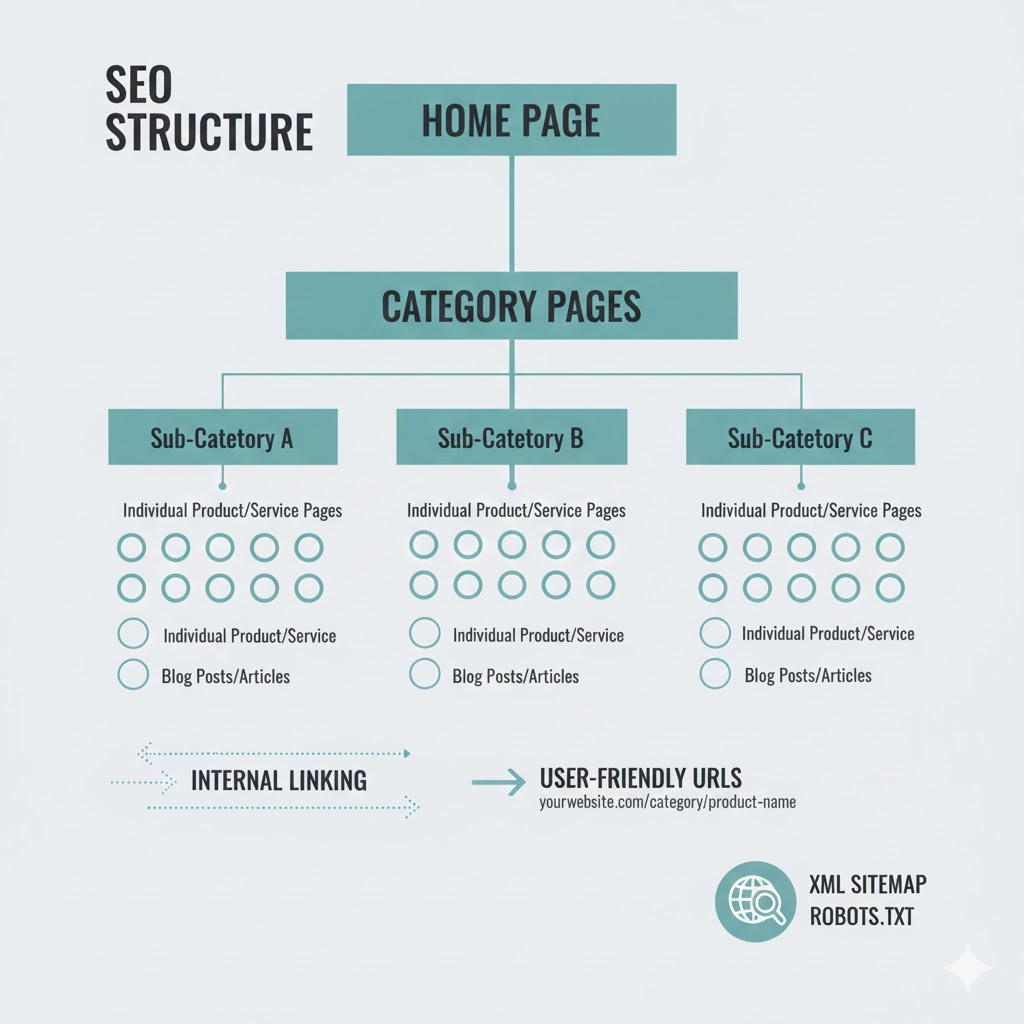
1. Start With a Clear Hierarchy
Every website needs a logical, three-level hierarchy:
-
Level 1: Homepage
-
Level 2: Category Pages (High-Level Topics)
-
Level 3: Subpages / Supporting Articles (Deep Content)
Search engines use this hierarchy to understand which pages hold the most authority.
Example (For a Student Building an Education Blog):
Home → Courses → SEO Course → On-Page SEO
This immediately tells Google:
-
“SEO Course” is more important than “On-Page SEO.”
-
“On-Page SEO” belongs under the SEO course category.
-
The site is likely education-related.
Think of this as the blueprint for your content. Without it, your site becomes an unrankable maze.
2. Build Topic Clusters for Semantic SEO
Google’s 2024–2025 updates heavily reward topical authority. Instead of publishing random articles, group your content around specific themes using topic clusters.
How Topic Clusters Work:
-
Pillar Page: A broad page covering a major topic
-
Cluster Pages: Detailed articles that link back to the pillar page
-
Internal Links: Connect all cluster pages in a web-like structure
Example Topic Cluster for “SEO Website Structure”:
-
Pillar Page: “SEO Website Structure Guide”
-
Cluster Pages:
-
Types of Website Architecture
-
Internal Linking Best Practices
-
Crawlability & Indexability
-
Breadcrumb Navigation
-
XML Sitemaps
-
Mobile Site Structure
-
This strategy helps:
-
Google understand your site’s expertise
-
Visitors explore more content
-
Your pages rank for long-tail and short-tail keywords
3. Use Human-First Navigation Menus
Simple, descriptive navigation menus improve usability and SEO. Google’s Quality Raters Guidelines (QRG) emphasize easy navigation as a trust signal.
Good Menu Example:
-
Courses
-
Blogs
-
Tutorials
-
Tools
-
Contact
Avoid Menu Mistakes:
-
Using vague labels like “Resources” for everything
-
Hiding important pages under dropdowns
-
Overloading menus with too many options
A rule of thumb: if users can’t find a page quickly, Google probably can’t either.
4. Create Clean, SEO-Friendly URLs
URLs should be:
-
Short
-
Descriptive
-
Lowercase
-
Keyword-focused
Example:
yourdomain.com/seo/website-structure
Avoid symbols, random numbers, or auto-generated slug strings.
5. Strengthen Internal Linking With Intent
Internal linking is the backbone of SEO website structure. It:
-
Helps Google discover pages
-
Distributes authority (PageRank)
-
Reinforces semantic relationships
-
Improves reader engagement
Internal Linking Best Practices:
-
Link from high-authority pages to new pages
-
Use descriptive anchor text
-
Avoid generic anchors like “click here”
-
Ensure every page has at least 2–5 internal links
-
Maintain a flat structure no page should be more than 3 clicks from the homepage
Professional SEOs treat internal linking like an art because it can dramatically shift your rankings.
6. Optimize for Crawlability and Indexability
Two essential technical elements:
Crawlability:
Google can access your pages.
Indexability:
Google can include your pages in search results.
Key Steps:
-
Use a clean robots.txt
-
Avoid blocking important pages
-
Fix crawl errors in Google Search Console
-
Remove duplicate content
-
Use canonical tags where necessary
A well-structured site reduces the “crawl budget” Google needs, which boosts your indexing speed.
7. Use Breadcrumb Navigation
Breadcrumbs show users exactly where they are on the site. Google loves them because they clarify URL hierarchy.
Example:
Home → SEO → Website Structure → Internal Linking
Breadcrumbs:
-
Reduce bounce rates
-
Improve internal linking
-
Enhance snippets in the SERP
8. Improve Site Speed and Mobile Structure
Google’s Core Web Vitals update makes performance a structural issue.
Checklist:
-
Compress images
-
Minimize JavaScript
-
Use responsive design
-
Avoid intrusive pop-ups
A slow website creates a broken user journey and poor structure is one of the main speed killers.
9. Add XML Sitemaps & HTML Sitemaps
XML Sitemap
Helps search engines understand your structure automatically.
HTML Sitemap
Helps visitors access important pages easily.
Both contribute to stronger indexation and clarity.
10. Avoid Duplicate or Thin Content Structure
Common mistakes students make:
-
Creating multiple pages about the same topic
-
Publishing low-value, short posts
-
Having orphan pages (no internal links)
Google’s 2024 Helpful Content system now penalizes websites with thin or duplicate structure-based issues. Focus on depth, usefulness, and originality.
Real-World Example: How Good Structure Improves SEO
A study by HubSpot found that websites using topic clusters improved their organic traffic by over 30% within six months. Similarly, Ahrefs reported that pages with strong internal link networks receive significantly higher rankings and faster indexation times.
Even Google’s own documentation states:
“A logical site structure helps our systems understand the importance and relationship of pages.”
For students building new websites, following these principles from day one gives your site a huge SEO advantage.
Actionable Step-by-Step Plan to Structure Your Website for SEO
Step 1: Identify 3–5 major categories
These form your top-level site architecture.
Step 2: Create pillar pages for each category
These will rank for competitive terms.
Step 3: Create 5–20 supporting articles
Each should link to the pillar page and to each other.
Step 4: Design your menu and footer
Make it easy, intuitive, and human-first.
Step 5: Optimize URL and internal link structure
Use descriptive slugs and strategic linking.
Step 6: Build XML and HTML sitemaps
Submit XML sitemaps to Google Search Console.
Step 7: Test with Google’s tools
Use PageSpeed Insights and Search Console to fix errors.
This is the same process used by agencies, SEO strategists, and successful website owners.
Conclusion
Your website structure is more than a technical detail it’s the foundation of your entire SEO strategy. When your structure makes sense, everything else becomes easier: ranking, indexing, user experience, and growth. Whether you're creating a personal project, class assignment, or professional portfolio, understanding SEO website structure gives you a long-term competitive edge.
As Google increasingly prioritizes semantic clarity and helpful content, students who master these principles early will be miles ahead in digital marketing, content strategy, and web development. If you start applying the strategies here — from topic clusters to internal linking you’ll create a website that feels natural to users and intuitive to Google.
Good structure doesn’t just help you rank. It helps you build trust.
FAQs
1. What is the best site structure for SEO?
A hierarchical structure with clear categories, pillar pages, and internal links works best for SEO and user experience.
2. How many clicks should it take to reach any page on my site?
Ideally, no more than three. This improves crawlability and usability.
3. Should I use subfolders or subdomains?
Subfolders are typically better for SEO because they consolidate authority.
4. What is a topic cluster?
A group of related articles linked to a pillar page that builds topical authority.
5. Do breadcrumbs improve SEO?
Yes they help users navigate and help search engines understand hierarchy.
Tags :
No Tags








0 Comments