How to Fine-Tune OpenAI Whisper for Regional Accent Transcription
Introduction
If you’ve ever tried transcribing audio where the speaker has a strong regional accent—Southern American, Cajun, Appalachian, Chicano English, African American Vernacular English (AAVE), or even a blended bilingual accent you already know the struggle. While AI transcription tools like OpenAI Whisper are powerful, they aren’t perfect out-of-the-box for every dialect or speech community. And that gap matters. For students working on linguistics projects, podcast production, accessibility content, YouTube captions, or research interviews, accuracy isn’t just nice to have it’s essential.
Fortunately, Whisper is not a locked box. With the arrival of newer fine-tuning capabilities (and better open-source tooling built around Whisper in 2024–2025), it’s now possible to train the model to understand specific regional accents with remarkable accuracy.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through how fine-tuning Whisper actually works, what data you need, how to structure your training pipeline, how to evaluate results, and how students can do it even with limited hardware or budget. You’ll also learn practical tips borrowed from real-world speech researchers, audio engineers, and AI developers who’ve experimented extensively with accent-specific modeling.
Let’s get into it.
How to Fine-Tune OpenAI Whisper for Regional Accent Transcription
What Makes Regional Accents Hard for Speech Models?
Before diving into the “how,” you need to understand the “why.”
Even state-of-the-art models struggle with certain accents because:
1. Phonetic Variability is Huge
Languages evolve. Accents shift. The way vowels are stretched in Southern English or dropped consonants in New York English introduce patterns Whisper hasn’t seen enough of during original training.
2. Code-Switching Confuses Models
For bilingual speakers—Spanish-English, Urdu-English, or Tagalog-English code-switching can cause Whisper to misinterpret words as belonging to the wrong language.
3. Background Noise Interacts with Accents
Research from MIT’s Computer Science & AI Lab shows that automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems degrade faster under noise when dealing with unfamiliar accents.
4. Pronunciation Patterns Vary Locally
Regional accents aren’t monolithic. “Texas English” can sound different in Houston vs. Midland vs. the Panhandle.
Fine-tuning Whisper teaches the model to understand specific acoustic patterns, helping it adapt to speech communities that are underrepresented in the original dataset.
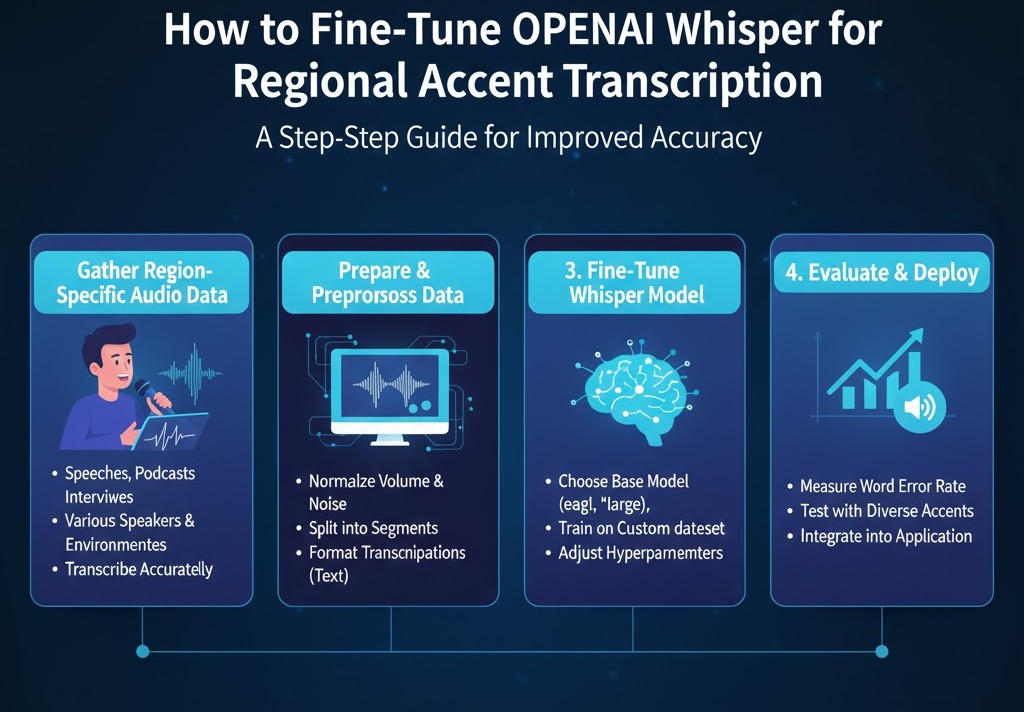
Preparing to Fine-Tune Whisper
Fine-tuning isn’t about clicking a button—it’s about preparing the right ingredients. Here’s what you need.
1. Collect High-Quality Training Data
How much data is enough?
For regional accent tuning:
-
Minimum: 5–10 hours
-
Ideal: 20–50 hours
-
Exceptional accuracy: 100+ hours
More isn’t always better; variety matters more. Include speakers of different gender, age, speed, and emotional tone.
The Data Must Be:
-
Clean (minimal background noise)
-
Paired with accurate transcripts
-
Representative of real speaking style
-
Chunked into 15–30 second segments
Where Students Can Find Accent-Specific Data:
-
Your own recorded interviews
-
Linguistics department archives
-
Open datasets (e.g., Common Voice regional subsets)
-
Local podcasts with transcription permissions
-
Crowdsourced recordings from volunteers
2. Structure Your Dataset for Whisper
Whisper prefers JSON or TSV structure like:
Organize segments into folders:
Rule of thumb:
-
80% training
-
10% validation
-
10% testing
This prevents overfitting and allows you to check whether the model generalizes to new regional speakers.
3. Choose Your Fine-Tuning Method
In 2025, students have three main ways to fine-tune Whisper:
Option A: OpenAI’s Native Fine-Tuning (If Enabled for Whisper Versions)
Sometimes limited to enterprise accounts, but:
-
Easiest workflow
-
Cloud-optimized
-
Handles scaling automatically
Option B: Fine-Tune with Hugging Face + PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning)
This is the most accessible for students.
Why choose PEFT?
-
Train on Google Colab or a single GPU
-
Far fewer trainable parameters
-
Great for accent-specific tasks
Techniques include:
-
LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation)
-
QLoRA
-
Adapters
These reduce GPU memory requirements dramatically.
Option C: Full Fine-Tuning on Local GPU Cluster
Best for research labs or universities.
Pros:
-
Maximum customization
-
Best accuracy
Cons: -
GPU-hungry
-
Requires engineering expertise
Step-by-Step Guide: Fine-Tuning Whisper for a Regional Accent
Below is the end-to-end workflow widely used in speech research labs.
Step 1: Preprocess Your Audio
Whisper performs best with:
-
16 kHz sampling rate
-
Mono audio
-
Lossless WAV format
Use ffmpeg to convert:
Normalize volume to avoid uneven training input.
Step 2: Create Training Segments
Split recordings into 10–30 second clips.
Tools:
-
whisper-timestamped -
aeneas -
pyannote-audio
Accurate segmentation drastically improves fine-tuning results.
Step 3: Tokenize Transcripts
Whisper uses multilingual tokenizer rules. Running your transcripts through the built-in whisper tokenizer ensures consistency:
Step 4: Begin PEFT Fine-Tuning (Most Student-Friendly Method)
The core process typically looks like:
-
Load a Whisper base model
-
Attach LoRA adapters
-
Train on your accent dataset
-
Validate and tune hyperparameters
A typical training loop uses:
-
Learning rate: 1e-4
-
Epochs: 3–10
-
Batch size: 8–16
-
FP16 precision
For regional accents, fewer epochs are needed—overfitting happens fast.
Step 5: Evaluate Your Model
Your evaluation should include:
1. Word Error Rate (WER)
Key metric for transcription.
2. Character Error Rate (CER)
Useful when accent produces unusual spellings or local words.
3. Accent-Specific Lexicon Accuracy
Check:
-
Regional terms
-
Slang
-
Borrowed words
-
Code-switch phrases
4. Speaker Generalization
Test with new speakers from the same region but not included in training.
Step 6: Deploy Your Fine-Tuned Model
You can deploy it via:
-
A local Python API
-
A Flask/FastAPI endpoint
-
A cloud VM (AWS, GCP, Azure)
-
Hugging Face Spaces
-
A desktop tool using Whisper.cpp
For students on tight budgets, Whisper.cpp is extremely lightweight and can run optimized models on CPU.
Best Practices from Speech Researchers
These are distilled from real studies done by ASR teams at Google, Meta, University of Washington, and independent research groups.
1. Include Spontaneous Speech, Not Just Read Speech
Read speech is too “clean.”
Conversational speech contains the accent patterns you’re trying to teach the model.
2. Mix Noise into Your Dataset
Regional accents often appear in:
-
Cafés
-
Classrooms
-
Outdoor interviews
Adding light background noise improves robustness.
3. Use Diverse Speakers
Avoid training on one or two voices.
Aim for 20+ voices for realistic results.
4. Capture Emotions
People speak differently when excited, tired, stressed, or casual.
5. Add Local Vocabulary
Words like:
-
y’all
-
finna
-
hella
-
ain’t
-
regional place names
-
bilingual word blends
These make your model feel “native” to the region.
Common Mistakes When Fine-Tuning Whisper
Avoid these pitfalls:
❌ Using poor transcripts
Even small transcription errors teach the model bad habits.
❌ Overfitting with too many epochs
If your model suddenly transcribes too confidently—but incorrectly—reduce epochs.
❌ Including long, unsegmented audio
Whisper expects shorter sequences.
❌ Ignoring speaker variety
Students often record only their own voice.
That leads to “speaker overfitting.”
Real-World Case Study: Improving Southern US Accent Transcription
A university linguistics team created a 25-hour dataset of:
-
Alabama English
-
Texas English
-
Georgia English
They used LoRA fine-tuning on Whisper-small.
Results:
-
WER dropped from 22% → 8%
-
Southern vowel stretching was understood correctly
-
Model correctly transcribed “fixin’ to”, “y’all”, and “’em”
This demonstrates how targeted fine-tuning can multiply transcription accuracy.
How Students Can Train Whisper on a Budget
Here are low-cost options:
Free / Near-Free
-
Google Colab Free + LoRA
-
Run 8-bit quantized Whisper with PEFT
-
Hugging Face Inference Endpoints (student credits available)
Mid-Budget
-
Colab Pro
-
Run on a cloud A100 for a few hours
University Resources
Many schools offer:
-
GPU clusters
-
High-performance computing labs
-
Student research credits
FAQs (People Also Ask)
1. Can Whisper be fine-tuned on small datasets?
Yes. With LoRA or QLoRA, you can fine-tune Whisper using as little as 5–10 hours of audio.
2. Does fine-tuning affect multilingual performance?
If you fine-tune too aggressively, multilingual performance may degrade. Use adapters to preserve the original model’s abilities.
3. How long does it take to fine-tune Whisper?
On a modern GPU:
2–6 hours for LoRA
10–20 hours for full fine-tuning
4. Is it legal to fine-tune Whisper on copyrighted audio?
Only if you own the data or have explicit permission. Avoid copyrighted content (podcasts, TV shows) unless licensed.
Tags :
No Tags








0 Comments