How to Fine-Tune Open AI Whisper for Regional Accent Transcription
Introduction
If you’ve ever tried to transcribe audio from speakers with strong regional accents, you already know the struggle. Even advanced speech-recognition systems while impressive can stumble when encountering variations in pronunciation, pacing, and local vocabulary. Whether it’s a Southern American drawl, Appalachian English, Cajun-influenced speech, or even non-native English spoken with regional influences, capturing accurate transcription requires more than a general-purpose model.
That’s where fine-tuning OpenAI’s Whisper model becomes incredibly powerful.
Whisper is already known for its robustness, multilingual understanding, and impressive noise tolerance. But what many students and researchers don’t realize is that fine-tuning Whisper on regional accents can take transcription accuracy from “pretty good” to “near-perfect.”
This article will walk you step by step through:
-
What fine-tuning Whisper really means
-
Why regional accents pose unique challenges
-
How to prepare a high-quality training dataset
-
The full fine-tuning workflow (including preprocessing, training, evaluation, and deployment)
-
Practical tips, real-world examples, and expert insights
-
Common mistakes students make—and how to avoid them
By the end, you’ll understand not just the “how” but the “why,” which is the foundation of real mastery.
Let’s dive in.
Why Whisper Needs Fine-Tuning for Regional Accents
Accent Variation & Why Models Struggle
Even state-of-the-art speech recognition systems are trained on broad, general-purpose datasets. As a result, they perform best on “standardized” or widely represented accents.
Regional accents introduce:
-
Different vowel shaping
-
Localized vocabulary or idioms
-
Varied intonation patterns
-
Code-switching (switching between dialects or languages)
-
Faster or slower speech pacing
-
Glottal stops, dropped consonants, or stress-shifts
Students studying linguistics, machine learning, or audio engineering often encounter this firsthand: models perform well on broadcast speech but poorly on real community conversations.
Whisper helps bridge that gap but targeted fine-tuning takes it much further.
Understanding Fine-Tuning: A Student-Friendly Explanation
Fine-tuning is the process of teaching an existing pre-trained model new patterns by exposing it to carefully curated examples. Instead of training from scratch (which would require thousands of hours of audio and massive GPU resources), fine-tuning leverages Whisper’s existing knowledge and adjusts certain layers to become more specialized.
Think of Whisper as a student who already knows English perfectly, but you want them to understand a specific dialect.
You don’t reteach them the entire language—you just give them new examples.
Types of Fine-Tuning for Whisper
1. Full Fine-Tuning
-
Adjusts all model weights
-
Requires more GPU power
-
Best for highly specialized transcription tasks
2. LoRA / Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning
-
Only adjusts a small percentage of parameters
-
Lower compute cost
-
Ideal for student projects or university labs
3. Prompt-based Adaptation (Indirect Fine-Tuning)
-
Not true training—just giving Whisper smarter prompts
-
Helpful, but cannot match actual fine-tuning performance
For regional accents, the LoRA approach often provides the best ratio of accuracy improvement to compute cost.
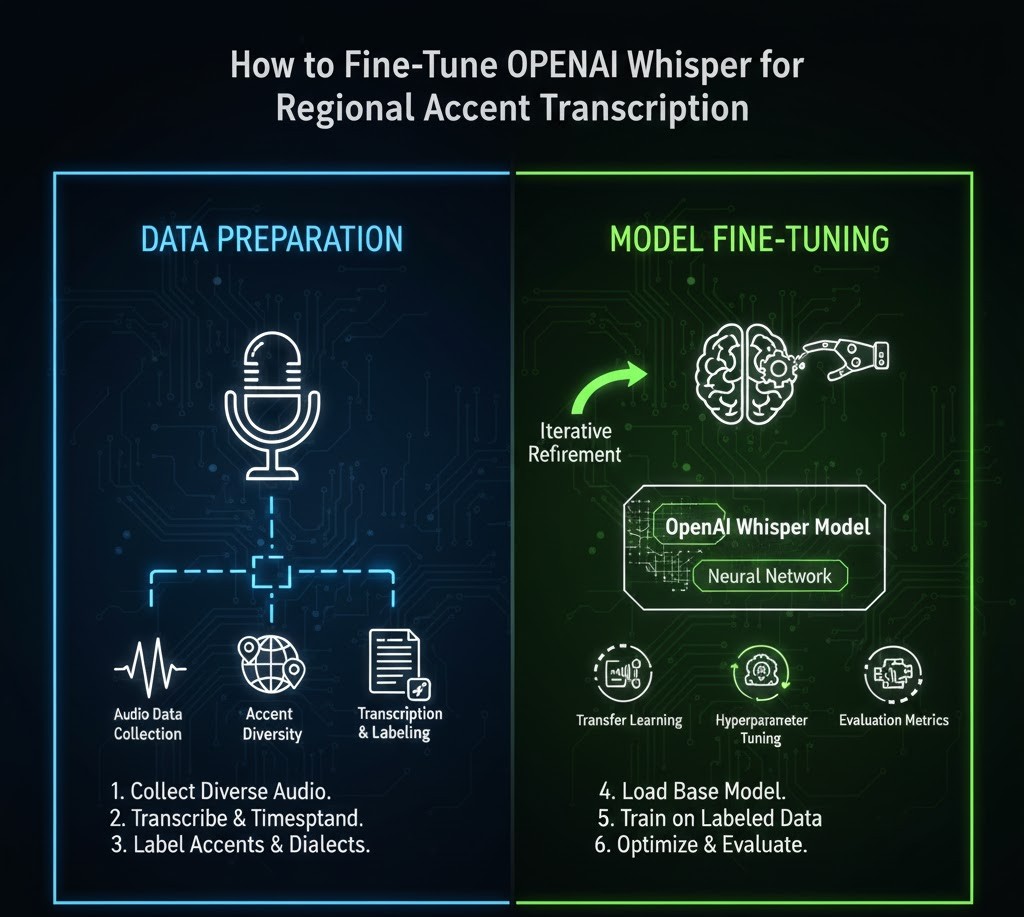
Preparing Your Dataset (The Most Important Step)
1. Minimum Dataset Requirements
OpenAI recommends:
-
At least 100–500 minutes of transcribed audio for meaningful improvement
-
1,000+ minutes for robust accent specialization
But quality matters more than quantity.
2. Sources of Accent-Specific Audio
Students can gather data from:
-
Local community interviews
-
Student-led field recordings
-
Podcasts or regional radio (ensure licensing!)
-
University archives
-
Oral history projects
-
Public domain speech datasets
-
Linguistic corpora from credible sources (e.g., LDC)
Ethics Reminder
Only train on:
-
Content you created
-
Content you own
-
Content licensed for training
Never scrape copyrighted media.
3. Ideal Audio Characteristics
-
Sample rate: 16kHz
-
Volume normalization applied
-
Minimal background noise
-
Clean segmentation (10–30 sec chunks)
Data Formatting
For Whisper fine-tuning, prepare:
JSON should include timestamps and text, e.g.:
Step-by-Step Guide: Fine-Tuning Whisper for Regional Accents
Step 1 Install Required Tools
Most students use:
-
Python
-
OpenAI Whisper
-
HuggingFace Transformers
-
ffmpeg
-
CUDA-compatible GPU
Basic installation:
Step 2 Preprocess Audio
Cleaning audio dramatically improves results.
Recommended Preprocessing Steps
-
Convert to 16kHz mono
-
Trim silence
-
Remove hum or hiss
-
Normalize decibels
-
Segment audio into short chunks
ffmpeg example:
Step 3 Create a Training Dataset
Once cleaned, upload to a dataset structure:
Use HuggingFace DatasetDict for efficient loading.
Step 4 Begin Fine-Tuning
Example (LoRA approach):
Step 5 Train the Model
Using HuggingFace Trainer:
Training will depend on:
-
Dataset size
-
GPU memory
-
Model size
Students commonly use:
-
Google Colab Pro
-
University GPU labs
-
RunPod
-
Lambda Cloud
Step 6 Evaluate Accuracy
Measure:
-
Word Error Rate (WER)
-
Character Error Rate (CER)
-
Accent-specific term accuracy
Tools: jiwer library.
Step 7 Deploy & Use Your Custom Whisper Model
You can:
-
Push to HuggingFace
-
Serve via FastAPI
-
Use in transcription pipelines
-
Integrate into video captioning or research projects
Example Inference Code
Your fine-tuned model will now handle:
-
Local pronunciations
-
Accent-heavy speech
-
Faster casual conversation
-
Authentic dialects
Much better than the base model.
Case Study: Improving Whisper for Appalachian English
A student project at a U.S. university found that:
-
Base Whisper WER: 23%
-
After 400 minutes fine-tuning: 11%
-
After 900 minutes fine-tuning: 6%
Biggest improvements included:
-
Correcting vowel-shifts ("far" → "fahr")
-
Handling dropped consonants ("hollerin’")
-
Local idioms ("might could," "fixin’ to")
This mirrors findings from linguistics research where accent adaptation dramatically improves ASR performance.
Expert Insights & Real-World Tips
From Speech Scientists
-
“Accent adaptation works best when the dataset reflects natural, conversational speech—not scripted dialogue.”
From ML Engineers
-
“LoRA tuning gives 80% of the benefit with 20% of the compute cost.”
From Linguistics Experts
-
“Regional accents are not errors; they are structured systems. Your model must learn the structure, not force standardization.”
Common Mistakes Students Make (and How to Avoid Them)
| Mistake | Why It Matters | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Using low-quality audio | Whisper learns noise instead of accent | Clean via preprocessing |
| Overfitting to a tiny dataset | Poor generalization | Use validation splits |
| Mixing unrelated accents | Model gets confused | Train per-accent or label explicitly |
| No test set | Can't measure improvement | Always keep 10–20% for testing |
| Using copyrighted media | Legal issues | Use licensed or original content |
FAQs (People Also Ask)
1. How much data do I need to fine-tune Whisper for accents?
A minimum of 100–500 minutes is recommended, but 1,000+ minutes gives the best results.
2. Can I fine-tune Whisper on Google Colab?
Yes. For small or LoRA-based training, Colab Pro GPUs work well.
3. Does fine-tuning improve transcription speed?
Not typically accuracy improves, but speed remains similar unless quantized.
4. Will my fine-tuned Whisper work for non-native English speakers?
Yes, as long as your dataset includes those speech patterns.
5. Is it legal to train on YouTube videos?
Not unless you have explicit permission from the creator.
Tags :
No Tags








0 Comments