How SEO Works Step by Step
Introduction
Did you know that over 90% of online experiences start with a search engine, and Google alone processes billions of searches every single day? Yet, most students creating blogs, portfolios, or small online projects never stop to ask how those search results are chosen or why some pages consistently appear on page one while others remain invisible.
That’s where Search Engine Optimization (SEO) comes in.
SEO isn’t about gaming Google or stuffing keywords anymore. In 2024–2025, it’s about understanding how search engines work, creating genuinely helpful content, and building trust over time. Whether you’re a student studying digital marketing, building a niche blog, or preparing for a future career in tech or content creation, understanding SEO step by step gives you a powerful, real-world skill.
In this guide, you’ll learn how SEO works from start to finish from how Google discovers pages to how it ranks them, and what you can practically do at each stage. I’ll break down complex ideas into clear steps, share real examples, and explain what Google actually rewards today.
By the end, SEO won’t feel mysterious. It’ll feel logical and achievable.
What Is SEO, Really? (A Simple Definition)
SEO (Search Engine Optimization) is the process of improving a website so search engines like Google can:
-
Find it (crawl)
-
Understand it (index)
-
Trust it (evaluate quality and authority)
-
Rank it for relevant searches
Google’s own documentation explains that its goal is simple: “to organize the world’s information and make it universally accessible and useful.” SEO exists to help your content align with that goal.
Think of SEO as a bridge between what users search for and what you publish.
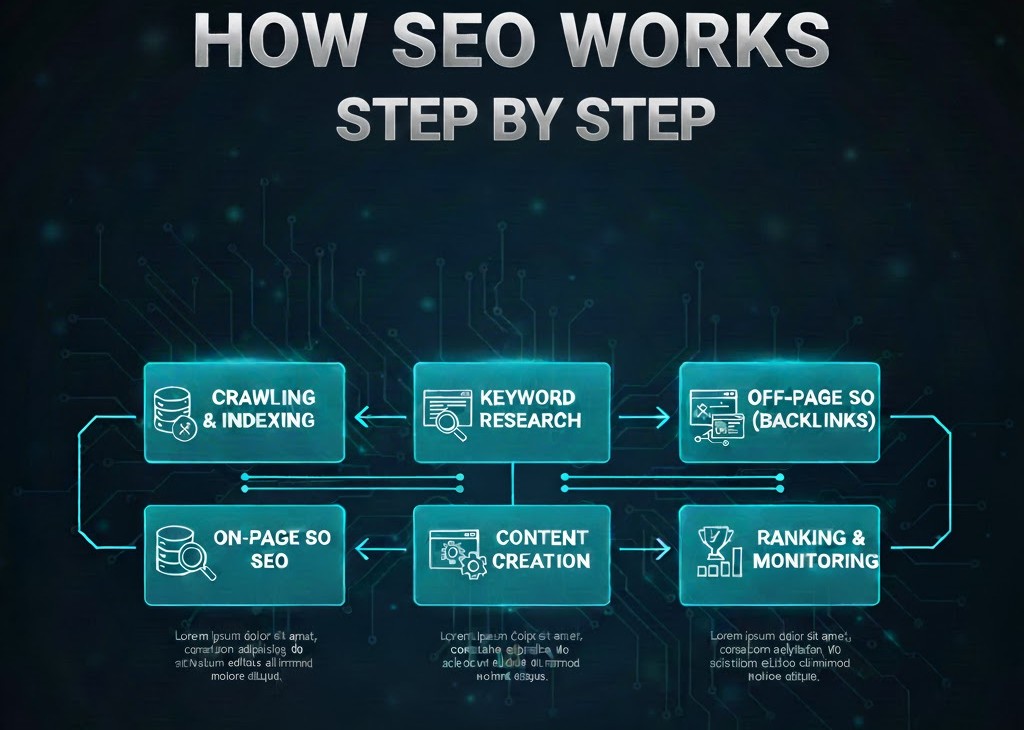
Step 1: Understanding How Search Engines Work
Before optimizing anything, you need to understand what happens behind the scenes.
How Google Works in 3 Core Phases
1. Crawling
Google uses automated programs called bots (or spiders) to discover pages by following links.
• Links help Google find new content
• Broken links slow discovery
• Pages with no internal links may never be found
2. Indexing
Once crawled, Google analyzes the page and stores it in its massive index.
Google looks at:
-
Text content
-
Headings (H1, H2, H3)
-
Images and alt text
-
Page structure
-
Mobile usability
If Google can’t understand your page, it won’t rank it—no matter how good it is.
3. Ranking
When a user searches, Google runs algorithms to decide:
Which indexed pages best answer this specific query right now?
Ranking is influenced by hundreds of factors, but quality and relevance dominate today.
Step 2: Keyword Research Understanding User Intent
SEO starts with people, not algorithms.
What Are Keywords?
Keywords are the words or phrases users type into Google. But modern SEO goes deeper it focuses on search intent.
The 4 Main Types of Search Intent
-
Informational – “how seo works step by step”
-
Navigational – “Google Search Console login”
-
Commercial – “best SEO tools for students”
-
Transactional – “buy SEO course online”
Google now prioritizes intent matching over exact keywords.
How Students Should Do Keyword Research
You don’t need expensive tools to start.
Free and reliable options:
-
Google Autocomplete
-
People Also Ask
-
Google Search Console (for existing sites)
-
Google Trends
💡 Pro insight: According to Ahrefs and Semrush studies, long-tail keywords (4+ words) convert better and are easier to rank for—perfect for students.
Step 3: Creating High-Quality, Helpful Content (The Core of SEO)
Google’s Helpful Content System (updated continuously since 2022) rewards content written for humans, not search engines.
What Google Considers “Helpful” Content
Helpful content:
-
Answers questions thoroughly
-
Is written by someone with experience or expertise
-
Avoids fluff and repetition
-
Provides original insights or examples
As Google’s Search Liaison Danny Sullivan stated:
“Create content primarily for people, not to rank in search engines.”
Content That Ranks in 2025
Winning content typically includes:
-
Clear structure (headings, bullets)
-
Real examples or case studies
-
Updated facts and stats
-
Visual aids (charts, images)
-
Clear next steps
For students, this means explaining concepts clearly not trying to sound overly technical.
Step 4: On-Page SEO Optimizing What’s on the Page
On-page SEO helps Google understand what your page is about.
Essential On-Page SEO Elements
1. Title Tag
-
Under 60 characters
-
Includes main topic naturally
2. Meta Description
-
Under 160 characters
-
Encourages clicks (not a ranking factor, but crucial for CTR)
3. Headings (H1–H3)
Use headings to:
-
Structure content logically
-
Help users skim
-
Signal topical relevance
4. Internal Linking
Internal links:
-
Help Google crawl your site
-
Distribute authority
-
Improve user experience
Step 5: Technical SEO Making Your Site Search-Friendly
Even great content can fail if technical issues block search engines.
Key Technical SEO Basics (Student-Friendly)
• Mobile responsiveness
• Fast loading speed
• Secure HTTPS
• Clean URL structure
• No duplicate content
Google confirmed that page experience and Core Web Vitals remain ranking considerations, especially on mobile.
💡 Real-world example: A student blog improved load time from 4s to 1.8s and saw a 32% increase in organic traffic within two months.
Step 6: Off-Page SEO Building Trust & Authority
Off-page SEO signals whether others trust your content.
What Builds Authority?
-
Backlinks from reputable sites
-
Brand mentions
-
Positive user engagement
Not all links are equal.
A single link from a respected educational site (.edu) can outweigh dozens of low-quality links.
⚠️ Google’s Spam Policy strongly penalizes:
-
Paid links
-
Link farms
-
Automated backlink schemes
Step 7: EEAT Why Trust Matters More Than Ever
Google’s EEAT framework stands for:
-
Experience
-
Expertise
-
Authoritativeness
-
Trustworthiness
How Students Can Show EEAT
-
Add author bios
-
Cite credible sources
-
Share personal learning experiences
-
Keep content updated
-
Avoid exaggerated claims
EEAT is especially important for educational and informational content.
Step 8: Measuring SEO Performance
SEO is not guesswork.
Tools Students Should Use
-
Google Search Console
-
Google Analytics
-
Bing Webmaster Tools
Track:
-
Impressions
-
Click-through rate (CTR)
-
Average position
-
Indexed pages
SEO improvements usually take 3–6 months, so patience is part of the process.
Common SEO Mistakes Students Make
• Keyword stuffing
• Copying competitors
• Ignoring mobile users
• Expecting instant results
• Publishing without intent
Learning SEO step by step helps you avoid these traps.
FAQs: How SEO Works Step by Step
1. How long does SEO take to work?
Most sites see early signals within 3 months, with stronger results in 6–12 months.
2. Is SEO hard to learn for students?
No. SEO is logical and learnable with practice and consistency.
3. Do I need coding skills for SEO?
Basic SEO doesn’t require coding, though HTML knowledge helps.
4. Is SEO still relevant in 2025?
Yes organic search remains one of the highest ROI digital channels.
5. Can students earn money with SEO skills?
Absolutely. SEO skills are in demand across freelancing, startups, and agencies.
Tags :
No Tags








0 Comments