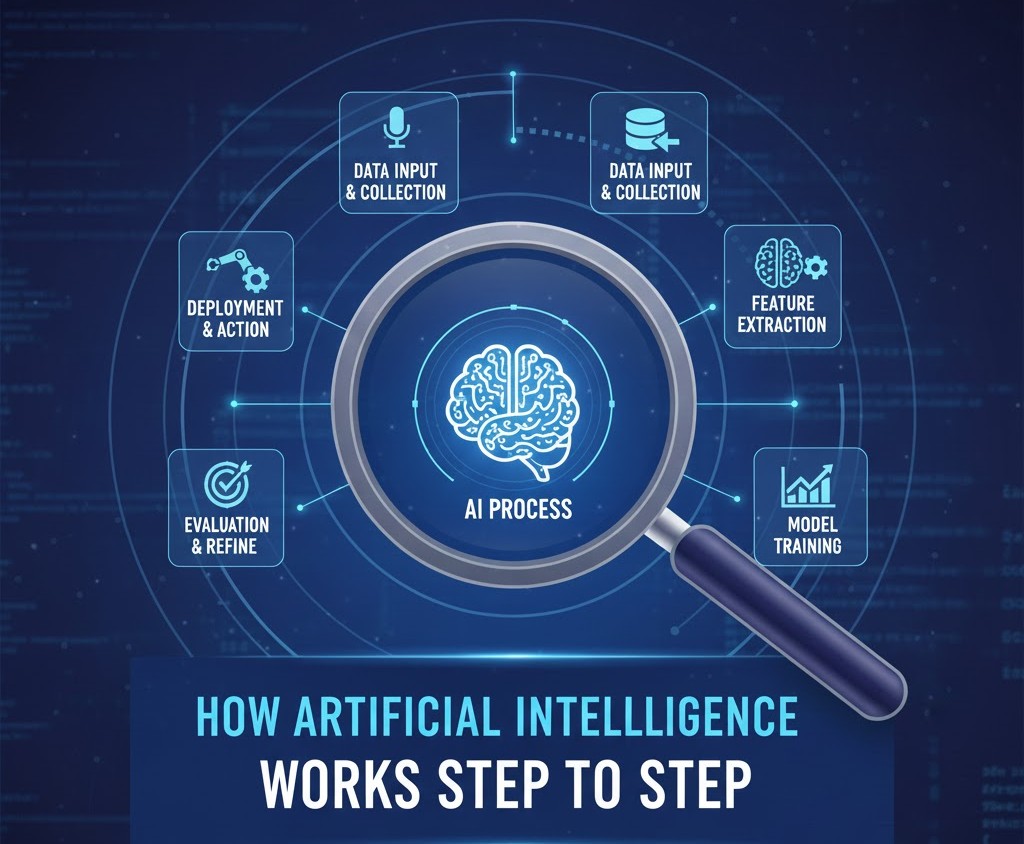
How Artificial Intelligence Works Step by Step
Introduction
Imagine unlocking your phone with your face, getting movie recommendations that actually match your taste, or asking a virtual assistant a question and receiving a clear answer in seconds. These everyday experiences all have one thing in common: artificial intelligence working quietly in the background. For students and beginners, AI can feel mysterious almost magical but it’s not magic at all. It’s a system built on logic, data, and carefully designed steps.
Understanding how artificial intelligence works is no longer just for engineers or computer scientists. AI is shaping careers in business, healthcare, education, marketing, finance, and nearly every modern industry. If you can grasp the basics of how AI functions step by step, you gain a valuable foundation for future learning and opportunities.
In this article, we’ll break down artificial intelligence in a clear, approachable way. You’ll learn what AI really is, how machines “learn,” how data moves through an AI system, and how decisions are made. By the end, you’ll understand AI not as a black box, but as a logical process built by humans one step at a time.
What Artificial Intelligence Really Means (Beyond the Buzzwords)
Artificial intelligence is often described as machines that “think like humans,” but that definition can be misleading. AI does not think, feel, or understand the world the way people do. Instead, it uses data and mathematical models to recognize patterns, make predictions, and support decisions.
At its core, AI is about solving problems. Humans design systems that can:
-
Identify patterns in large amounts of data
-
Learn from past examples
-
Make predictions or recommendations
-
Improve performance over time
AI comes in different forms, from simple rule-based systems to advanced models that learn from millions of data points. What connects all of them is a structured process that turns raw information into useful output.
To understand AI properly, we need to look at how it works step by step.
Step 1: Defining the Problem AI Is Meant to Solve
Every AI system starts with a clearly defined goal. Before any code is written or data is collected, humans decide what problem the AI should help solve.
Examples include:
-
Predicting whether an email is spam
-
Recognizing faces in photos
-
Recommending products to users
-
Translating text between languages
This step is critical because AI systems are not general thinkers. Each one is designed for a specific task. An AI trained to recognize images cannot suddenly start predicting stock prices without being redesigned and retrained.
Beginner takeaway: AI doesn’t “figure things out on its own.” Humans define the task first.
Step 2: Collecting and Preparing Data
Data is the fuel of artificial intelligence. Without data, AI cannot learn or make accurate decisions.
What kind of data does AI use?
Depending on the task, data may include:
-
Text (articles, messages, reviews)
-
Images and videos
-
Audio recordings
-
Numbers (sales figures, temperatures, scores)
For example, an AI that recognizes handwritten numbers needs thousands or millions of examples of handwritten digits.
Why data preparation matters
Raw data is often messy. It may contain errors, missing values, or irrelevant information. Before feeding data into an AI system, it must be:
-
Cleaned (fixing errors and inconsistencies)
-
Organized into a usable format
-
Labeled (in many cases)
If the data is poor quality, the AI’s results will also be poor. This is why people often say, “AI is only as good as the data it learns from.”
Beginner takeaway: Most of the work in AI happens before learning even begins.
Step 3: Choosing the AI Model
Once the problem and data are ready, developers choose a model. A model is a mathematical structure that processes input data and produces output.
Common types of AI models
-
Rule-based systems: Follow predefined rules (used in early AI)
-
Machine learning models: Learn patterns from data
-
Deep learning models: Use layered structures inspired by the human brain
For beginners, the key idea is this:
A model is the logic engine that connects data to decisions.
Different problems require different models. A system that detects fraud uses a different approach than one that generates text or recognizes speech.
Beginner takeaway: The model is not the data and not the answer it’s the mechanism that learns from data.
Step 4: Training the AI (How Machines Learn)
Training is where artificial intelligence actually “learns.”
During training:
-
Data is fed into the model
-
The model makes a prediction or output
-
That output is compared to the correct answer
-
The model adjusts itself to reduce errors
This process repeats many times sometimes millions of times until the model’s predictions improve.
A simple example
Imagine teaching a child to recognize cats:
-
You show a picture
-
You say “This is a cat”
-
The child makes mistakes at first
-
Over time, the child learns patterns
AI training works similarly, but instead of understanding, it adjusts numbers inside the model to improve accuracy.
Beginner takeaway: AI learning is based on repetition, feedback, and adjustment not understanding.
Step 5: Testing and Validation
After training, the AI is tested using new data it has never seen before. This step checks whether the system can generalize its learning rather than memorizing examples.
Testing helps answer questions like:
-
Is the AI accurate?
-
Does it perform well in real-world conditions?
-
Does it make consistent mistakes?
If performance is poor, developers may:
-
Improve the data
-
Adjust the model
-
Redefine the problem
This step prevents unreliable or biased systems from being deployed too early.
Beginner takeaway: A trained AI is not automatically a good AI it must be tested carefully.
Step 6: Deployment in the Real World
Once an AI system performs well in testing, it is deployed. This means integrating it into apps, websites, devices, or business systems.
Examples include:
-
Search engines ranking results
-
Streaming platforms recommending content
-
Banks detecting suspicious transactions
-
Healthcare systems assisting with diagnosis
At this stage, AI starts interacting with real users and real data.
Step 7: Learning and Improving Over Time
Many AI systems continue learning after deployment. They collect new data, monitor performance, and adapt to changing conditions.
This ongoing improvement is essential because:
-
User behavior changes
-
Language evolves
-
New patterns emerge
Human oversight remains important. Engineers monitor results, fix issues, and ensure ethical and responsible use.
Beginner takeaway: AI is not “set and forget.” It evolves with supervision.
How Artificial Intelligence Fits Into Everyday Life
AI is not one single technology—it’s a collection of systems working behind the scenes.
You encounter AI when:
-
A navigation app suggests a faster route
-
A job portal recommends roles based on your profile
-
An online store personalizes your homepage
-
A grammar tool improves your writing
Understanding how AI works step by step helps you use these tools more critically and confidently.
Common Myths Beginners Believe About AI
Many students start with misconceptions that can slow learning.
-
Myth: AI thinks like humans
Reality: AI processes data, not thoughts -
Myth: AI is always objective
Reality: AI reflects the data it learns from -
Myth: You must be a coding genius to understand AI
Reality: Conceptual understanding comes first
Clearing these myths makes AI easier to approach.
Practical AI Skills Students Can Start Learning Today
You don’t need advanced math or programming right away. Beginners can focus on:
-
Understanding how data is used
-
Learning basic machine learning concepts
-
Studying real-world AI applications
-
Practicing logical problem-solving
These skills build a strong foundation for future specialization.
How AI Careers and Opportunities Are Evolving
AI-related roles are growing across industries. Beyond engineering, opportunities include:
-
Data analysis
-
AI product management
-
Digital marketing and personalization
-
Ethics and policy
-
Education and training
Understanding how AI works step by step gives students a long-term advantage, even if they don’t become developers.
FAQs: Artificial Intelligence Explained Simply
How does artificial intelligence learn?
AI learns by analyzing data, making predictions, and adjusting its model based on feedback to reduce errors.
Is artificial intelligence the same as machine learning?
No. Machine learning is a subset of AI focused on learning from data. AI is the broader concept.
Does AI require human supervision?
Yes. Humans design, train, test, and monitor AI systems to ensure accuracy and responsibility.
Can AI work without data?
No. Data is essential for AI systems to learn and function effectively.
Is AI replacing human jobs completely?
AI changes how work is done, but it also creates new roles and opportunities.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence may sound complex, but when broken down step by step, it becomes far more approachable. From defining a problem and collecting data to training models and improving performance over time, AI follows a logical, human-designed process. It doesn’t think or feel it calculates, predicts, and adapts based on patterns.
For students and beginners, understanding how artificial intelligence works is not about becoming an expert overnight. It’s about building clarity, confidence, and curiosity. AI is shaping the future of work, education, and technology, and those who understand its foundations will be better prepared to participate in that future.
As you continue learning, remember this: AI is a tool created by humans. The more you understand how it works, the more effectively and responsibly you can use it.
Tags :
No Tags








0 Comments